The course typically covers a range of topics related to administrative law, including:
Introduction to Administrative Law: An overview of the nature, scope, and historical development of administrative law, including its relationship with constitutional law and other branches of law.
Principles of Administrative Law: The fundamental principles underlying administrative law, such as the rule of law, natural justice, fairness, reasonableness, proportionality, and the separation of powers.
Administrative Decision-Making: The legal framework governing administrative decision-making processes, including the role of administrative agencies, the exercise of discretionary powers, and the duty to provide reasons for decisions.
Judicial Review: The concept of judicial review and its significance in administrative law. This involves studying the grounds on which administrative decisions can be challenged in courts, the procedures for seeking judicial review, and the remedies available.
Administrative Tribunals: The role and functions of administrative tribunals, including their jurisdiction, powers, procedures, and the principles of natural justice applicable to tribunal hearings.
Administrative Law and Human Rights: The interaction between administrative law and human rights, including the protection of individual rights in administrative proceedings and the compatibility of administrative actions with constitutional rights.
Ombudsman and Administrative Redress: The role of ombudsman institutions in addressing grievances and complaints against administrative bodies, as well as the mechanisms for seeking administrative redress.
Administrative Law and Public Policy: The influence of administrative law on the formulation and implementation of public policies, including the role of administrative agencies in policy-making and the legal control of administrative discretion.
Administrative Law in Practice: Practical aspects of administrative law, such as drafting legal documents, preparing submissions, and conducting administrative law litigation.
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY

Cource is designed for the preperation of UGC NET for the law students.
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY

Course offered by: Nikhilesh N, BA (Law) LL.B, LL.M (Maritime Law and Administrative Law), Pursuing Ph.D on International Criminal Law.
Course discusses all the elementary aspects of public international law including the Subject Matter of International law, International organisations, Law of the Sea, International humanitarian law, etc.
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY

International criminal law
It includes war crimes, crimes against humanity, genocide, and the crime of aggression. These crimes are also referred to as international criminal law stricto sensu. They are considered the gravest crimes of concern to the international community and are prohibited because they threaten international peace and security and fundamental human rights.
Transnational criminal law
Transnational crimes transcend international boundaries. Under article 3(2) of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organised Crime 2000, an offence is transnational if it is committed in:
- More than one state,
- One state, but a substantial part of the preparation takes place in another state,
- One state, but involves an organised criminal group that engages in criminal activities in more than one state, or
- One state, but has substantial effects in another state.
Transnational crimes include organised crimes, drug trafficking, human trafficking, corruption, terrorism, terrorism financing, and piracy.
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY

Faculty: Dr. Nikhilesh N
Assistant Professor of Law
School of Legal Studies, Kannur University
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY

About Faculty: Have 9 years of Experience in LL.M Teaching.
About the course: Forensic science encompasses a broad field of scientific knowledge in pursuit of crime and the criminal. The course will give an overview of the Scientific methods of adducing evidence in present-day society.
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY
- Teacher: Sheeja J FACULTY

Aims:
• To acquaint the students with the distinctive qualities of imaginative writing, such as novels and short fiction, their complex history of development, and the reasons for the abiding popularity of these genres.
Objectives:
• The student will learn to analyze the effectiveness of complex elements of the plot, such as setting, major events, problems, conflicts, and resolutions.
• The student will be enabled to understand the novel in the context of its pre-modern history as well as its modern international form.
• The student will be offered a masterful insight into basic values of human nature that abide in the fictional form.
Literary TermsFrom Literary Terms and Criticism – John Peck and Martin Coyle) 18th-century novels,
Narrative structure, Tales, Fables, Parables Narrator, Realism, Reflexive Novel, Utopian and Science Fiction, Gothic Novel, Stream of Consciousness, Magical Realism.
- Teacher: NIKHILESH N FACULTY
- Teacher: Shruthi A K Dasan FACULTY
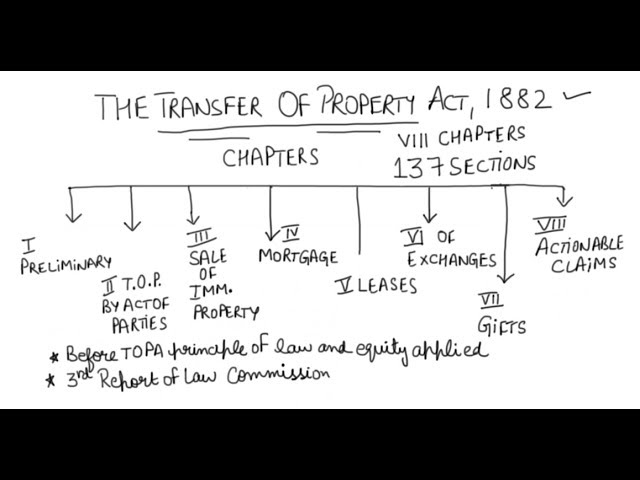
This paper gives an overview of the transfer of property act and other laws connected to the property.
- Teacher: PRESANNAKUMARI E S FACULTY
